+86-13928321129
jiahewell@jhzhb.com
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
 English
English English
English
Thermal Conductivity
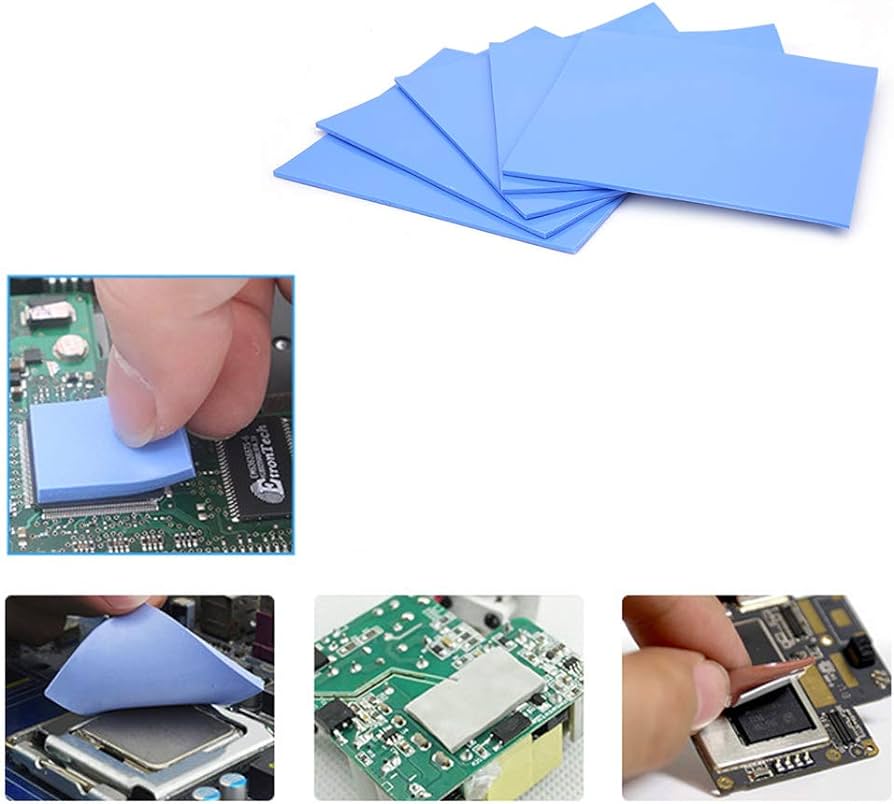
The higher the thermal conductivity, the better a material can transfer heat. Thermal conductive silicone typically ranges from 0.5W/m·K to 6W/m·K. For devices that need to shed a lot of heat, like LED lights, computer motherboards, and power amplifiers, choosing silicone with higher thermal conductivity is key.
Temperature Range
Most thermal conductive silicone works well in temperatures between -40°C and 200°C. Some high-end options can handle even higher temperatures, making them perfect for extreme conditions. When choosing, make sure to consider the temperature needs of your device to ensure the silicone will perform properly.
Compression Performance
Good compression performance means the silicone can maintain stable contact under pressure, which is essential for efficient heat transfer. Compression rates can vary, so it’s important to select the right type of silicone based on your device's specific needs.
Electrical Insulation
While the main job of thermal conductive silicone is heat dissipation, its electrical insulation properties are also important, especially in cases where electrical short circuits need to be avoided.
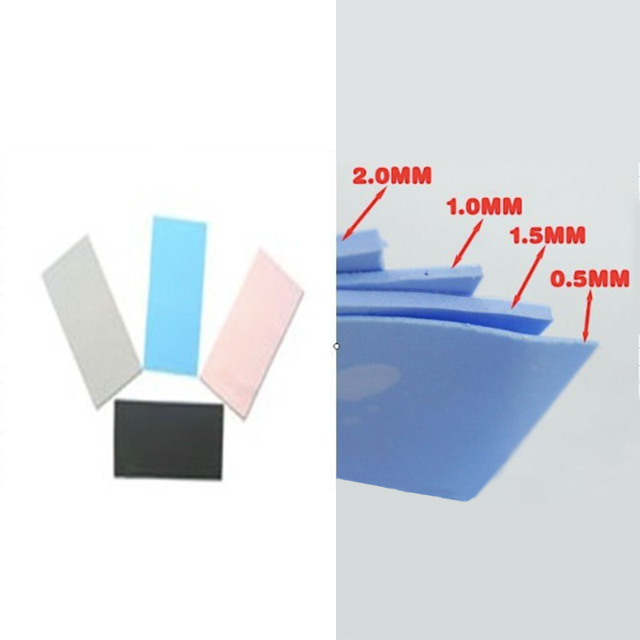
Thickness and Suitability
Thermal conductive silicone comes in different thicknesses and can be customized based on your device’s heat management needs. Thinner silicone works well for small devices or tight spaces, while thicker options are better for larger devices or high-power applications.
Durability and Aging Performance
High-quality thermal conductive silicone holds up well over time, even with temperature fluctuations or pressure. However, how well silicone ages can vary by brand and type, so it’s important to check the product’s lifespan to make sure it stays reliable in the long term.
By understanding the key features of thermal conductive silicone, you can choose the best type for your device, ensuring effective heat dissipation and long-lasting performance.