+86-13928321129
jiahewell@jhzhb.com
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
 English
English English
English
In the heat dissipation management of electronic products, Thermal Grease and Thermal Paste are two commonly used thermal conductive materials. This article will analyze the differences between thermal grease and thermal paste in detail to help you better choose the right material.
1. Definition and composition
Thermal Grease
Thermal Grease is a silicon-based thermal conductive material, usually a mixture of silicone oil and thermal conductive fillers. The main advantage of Thermal Grease is good fluidity, which can effectively fill the tiny gap between the radiator and the electronic components and enhance thermal conduction.

Thermal Paste
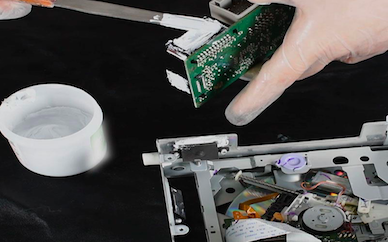
Thermal paste is a viscous thermal conductive material, usually composed of organic compounds, metal oxides and other fillers. The main ingredients and formula of thermal paste may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. Usually, its viscosity is relatively high, which can provide good adhesion and prevent displacement between the radiator and the component.
2. Thermal conductivity
Thermal Grease has good fluidity and can effectively fill the uneven surface, thereby increasing the thermal contact area and enhancing the thermal conduction efficiency.
The thermal conductivity of thermal grease varies depending on its composition and production process, and can usually reach 2 to 8 W/m·K.
3. Usage scenarios
Thermal Grease
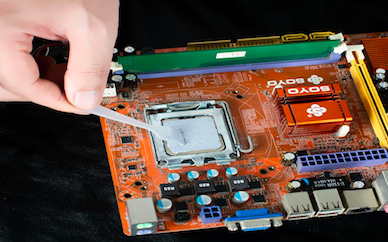
Due to its excellent fluidity and stability, Thermal Grease is suitable for most electronic components, especially the heat dissipation management of high-power devices such as CPUs and GPUs.
Thermal Grease
Due to its high viscosity, thermal grease is suitable for scenarios that require stronger adhesion, such as heat sinks and components that need to be fixed for a long time.
4. Temperature range and lifespan
Thermal Grease performs well in high temperature environments and can usually withstand operating temperatures up to 200°C. Thermal grease may have a wider temperature range, but its long-term performance may be affected by organic components, resulting in aging and reduced thermal conductivity.