+86-13928321129
jiahewell@jhzhb.com
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
 English
English English
English
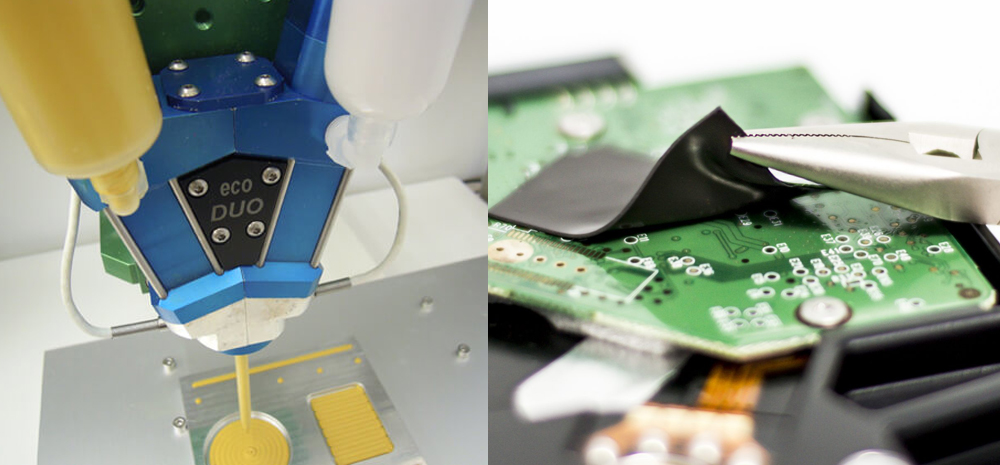
Thermal grease is a material widely used in electronic devices, heat sinks, and other fields that require effective heat conduction. Its main function is to fill the tiny gaps between contact surfaces, thereby improving the efficiency of heat transfer.
Thermal conductivity is the core indicator for measuring a material's ability to conduct heat. High-quality thermal grease typically has a thermal conductivity between 0.5 and 5 W/m·K, making it suitable for high-performance electronic devices.

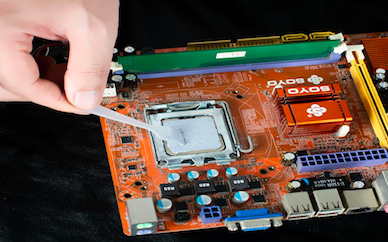
Viscosity refers to the fluidity of thermal grease, usually expressed in "Pa·s." An appropriate viscosity ensures that the grease is easy to apply while maintaining good stability after curing.
The working temperature range of thermal grease indicates the temperatures at which it can effectively operate. High-quality thermal grease generally has a working temperature range of -50°C to 200°C, allowing it to adapt to various environmental conditions.
Voltage resistance is the ability of thermal grease to withstand a certain voltage without breaking down. This indicator is particularly important for electrical equipment.
Density affects the amount of thermal grease needed and the effectiveness of heat dissipation. Typically, higher density leads to better thermal conductivity, but excessive density may make application difficult.
High-quality thermal grease resists oxidation under high temperature and humidity conditions, maintaining good thermal conductivity over time.
By understanding key performance indicators such as thermal conductivity, viscosity, working temperature range, voltage resistance, density, and aging resistance, consumers can choose the right thermal grease for their specific needs. This ensures the stable operation and longevity of electronic products. Selecting high-quality thermal grease will help enhance the performance and safety of devices.
